In recent years, shockwave therapy has gained popularity as a non-invasive treatment option for various musculoskeletal conditions. This innovative medical technique utilizes high-energy sound waves to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and alleviate pain. Whether you’re an athlete recovering from an injury or an individual seeking relief from chronic pain, this guide aims to provide you with a comprehensive overview of shockwave therapy.
Understanding Shockwave Therapy
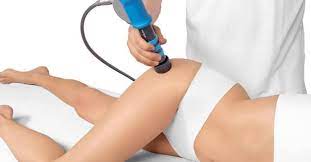
Shockwave therapy, also known as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), involves the application of acoustic pressure waves to the affected area. These high-energy sound waves are generated by a specialized device and transmitted through the skin to targeted tissues. The waves create microtrauma, promoting increased blood circulation, cell regeneration, and the release of growth factors, ultimately enhancing the body’s natural healing response.
Common Applications: Shockwave therapy is utilized to treat a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions. It has shown promising results in the management of conditions such as:
- Plantar fasciitis and heel spurs
- Achilles tendinopathy
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
- Golfers elbow (medial epicondylitis)
- Patellar tendinopathy (jumper’s knee)
- Rotator cuff tendinopathy
- Calcific tendonitis
- Myofascial trigger points
- Shin splints
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy:
- Non-invasive: Shockwave therapy is a non-surgical and non-invasive treatment option, making it a favorable choice for individuals seeking alternatives to more invasive procedures.
- Fast and efficient: Treatment sessions are typically short, lasting approximately 10-20 minutes, and most patients experience relief after just a few sessions.
- Minimal side effects: Shockwave therapy is generally safe and well-tolerated, with minimal side effects reported. Some patients may experience mild discomfort during treatment or temporary skin reddening.
- Enhanced healing: The therapy stimulates blood flow, accelerates tissue repair, and promotes collagen production, aiding in the healing of damaged tissues.
- Reduced reliance on medication: Shockwave therapy can reduce the need for pain medications or invasive treatments, providing a more holistic approach to pain management.
The Treatment Process
The shockwave therapy process typically involves the following steps:
- Assessment: A thorough assessment is conducted to evaluate the condition, determine its suitability for shockwave therapy, and create an individualized treatment plan.
- Application of shockwaves: The practitioner applies the shockwaves to the affected area using a handheld device. The intensity and frequency of the waves are adjusted based on the specific condition and patient’s tolerance.
- Treatment sessions: The number of treatment sessions can vary depending on the condition and individual response. Usually, multiple sessions are recommended, spaced a week or more apart.
- Post-treatment care: Following each session, the practitioner may provide guidance on self-care techniques, such as exercises, stretching, or icing, to complement the treatment and promote optimal recovery.
Seeking Professional Care
It is crucial to consult a qualified healthcare professional, such as a physiotherapist, chiropractor, or orthopedic specialist, before considering shockwave therapy. They will assess your condition, discuss treatment options, and determine whether shockwave therapy is suitable for you.
Potential Considerations and Contraindications
While shockwave therapy is generally safe, there are certain considerations and contraindications to be aware of. Individuals with the following conditions may require careful evaluation or avoid shockwave therapy altogether:
- Pregnancy
- Blood clotting disorders or use of anticoagulant medications
- Open wounds or infections at the treatment site
- Tumors or cancer
Visit Bend Total Body Chiropractic for your next shockwave therapy in Bend, Oregon.